Purchasing a vehicle is a major life milestone, but for most, it also represents a significant long-term financial commitment. While the prospect of driving home a new car is exciting, the complexities of financing, specifically understanding the vehicle loan and EMI process can be overwhelming. This guide serves as a practical automobile roadmap to help you navigate interest rates, calculation logic, and repayment strategies with confidence.
Introduction
A vehicle loan is a structured financial tool where a lender provides the capital needed to purchase a car or two-wheeler upfront. In exchange, you agree to repay this amount over a fixed period through Equated Monthly Installments (EMIs). These payments are vital for managing personal cash flow, as they transform a massive one-time expense into predictable monthly outgoings. Until the debt is cleared, the vehicle typically serves as collateral for the lender.
Key Factors to Consider
Before signing a loan agreement, evaluate these critical elements to ensure the deal aligns with your financial health:
- Loan-to-Value (LTV) Ratio: Lenders often fund 80% to 90% of a car’s on-road price, though those with exceptional credit may qualify for 100% financing.
- Down Payment: Paying more upfront reduces your principal loan amount, which leads to lower interest costs and more manageable EMIs.
- Credit Score: In India, a CIBIL score of 700+ is generally the benchmark for securing faster approvals and competitive interest rates.
- Total Cost of Ownership: Remember that your monthly budget must cover not just the EMI, but also insurance, fuel, and ongoing maintenance.
Detailed Breakdown: The Loan and EMI Process
The Car Loan Procedure
The journey from application to ownership typically follows five steps:
- Application: You provide personal and financial details to a bank or dealer.
- Documentation: You must submit identity, address, and income proofs, such as salary slips or ITR filings.
- Credit Evaluation: Lenders perform authenticity audits and credit checks to assess your repayment capacity.
- Final Approval: Once the lender is satisfied, the specific loan terms are finalized.
- Disbursal: The funds are sent directly to the dealer or seller to complete the purchase.
EMI Calculation Logic
Every EMI consists of two parts: the principal (the actual loan repayment) and the interest (the cost of borrowing). Initially, a larger portion of your monthly payment goes toward interest; as the principal balance drops, the interest component decreases accordingly.
The standard formula used for this calculation is:
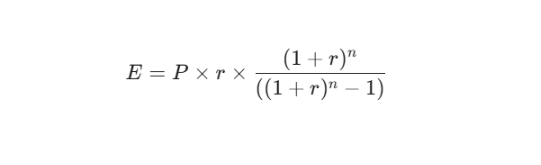
- E = EMI amount
- P = Principal loan amount
- r = Monthly interest rate (Annual rate / 12 / 100)
- n = Loan tenure in months
Pros & Cons
Interest Rate Types
- Fixed Rate: Offers total predictability as EMIs remain constant, though the starting rate is often higher.
- Floating Rate: Often starts lower and can save money if market rates drop, but EMIs can increase if benchmark rates rise.
Loan Tenure Impact
- Longer Tenure: Results in lower, more affordable monthly EMIs but leads to much higher total interest paid over the life of the loan.
- Shorter Tenure: Requires higher monthly payments but significantly reduces the overall cost of borrowing.
Expert Tips for Smart Financing
- Shop Direct: Approach banks directly rather than only relying on dealer financing to potentially secure lower processing fees and better terms.
- The 35% Rule: Aim to keep your total EMI obligations below 30–35% of your monthly income to maintain financial stability.
- Strategic Prepayments: Use bonuses or windfalls to make partial prepayments. If foreclosure fees are low, this is the most effective way to reduce your interest burden.
- Enable Auto-Debit: Set up automated payments to ensure you never miss a deadline, which protects your credit score from damage.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Focusing Only on EMI: Don’t be lured by a low monthly payment that hides a very long tenure and excessive interest.
- Ignoring the Fine Print: Always check for hidden charges, such as processing fees, or high penalties for early loan closure.
- Financing Add-ons: Dealers may suggest adding insurance or accessories into the loan; this only increases your interest burden unnecessarily.
- Mass Applications: Applying with multiple lenders simultaneously can trigger hard credit inquiries and lower your score.
FAQs
Q: Can I change my EMI amount later?
A: Some lenders offer “step-up” (increasing over time) or “step-down” (decreasing over time) plans to match your income growth.
Q: Does the car model affect the interest rate?
A: Yes. Interest rates can vary based on whether the vehicle is new or used, with used cars generally attracting higher rates.
Q: Is paying off the loan early a good idea?
A: Generally yes, but be aware that some lenders charge foreclosure fees ranging from 5% to 6% of the outstanding principal.
Final Verdict
Securing the right vehicle loan is just as critical as choosing the right car. By realistically planning your EMIs, comparing lender terms, and maintaining a disciplined repayment schedule, you can turn your ownership dream into a sound financial reality.



